What is ACARS?
ACARS is an acronym for Aircraft Communications Addressing and Reporting System which is a digital communications system that aircraft use to send and receive short messages to and from ground stations.
Standard ACARS transmits at a frequency of 131.550MHz, which is squarely in the receivable range of the RTL-SDR. The RTL-SDR software radio can be used as a radio scanner for listening to these digital messages, and with the help of some decoding software, can be used to decode and display the messages. The messages you can receive will be from nearby aircraft and ground stations. Most messages will be unreadable data intended for computers, but you can find out what is flying near you by decoding the flight number and aircraft registration details sent with every message.
There is also HF ACARS, which is used for long distance communications. In this article the focus will be on VHF ACARS, as receiving HF ACARS is a little different.
Examples of RTL-SDR used to decode ACARS
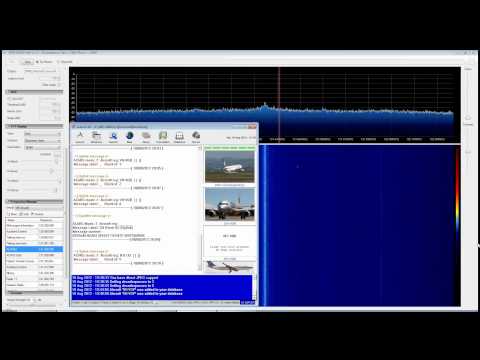
YouTube user Superphish shows a timelapse over 5 hours of ACARS traffic and decoding using SDR# and decoding program acarsd. He used a J-Pole antenna.
YouTube user moonfestmadness shows another RTL-SDR video also with SDR# and decoding program acarsd. You can also hear what ACARS sounds like in this video.
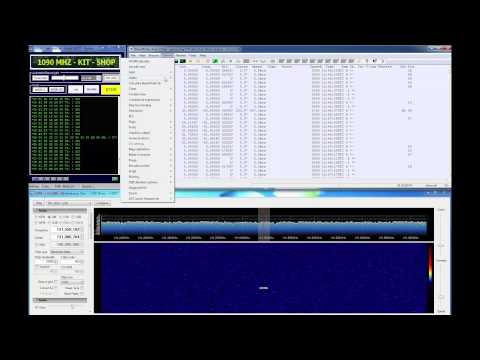
In this video, hamradioscience uses multiple RTL-SDR dongles to add ADS-B and ACARS decoding to PlanePlotter.
Tutorial – Decoding ACARS using SDRSharp and RTL-SDR
We will assume you have bought and set up RTL-SDR with SDRSharp. If you have not bought an RTL-SDR yet, see the buy RTL-SDR page and then the quickstart guide.
You will also need to have an audio piping method set up. Either first set up windows stereo mix, or download and install virtual audio cable (paid with trial) or the free VB-Cable. Ensure the audio method you use in SDRSharp is set to the default audio device in the windows recording audio settings.
If you are unfamiliar with ACARS signals, an example of the waterfall produced by ACARS signals is shown on the left. An audio example is also provided below.
Now to decode ACARS follow these steps.
- Open SDRSharp, and set the output audio device to the audio piping method you intend to use.
- Tune to an ACARS frequency. Use a bandwidth of around 5-10 kHz, 6 kHz works best for me. The main ACARS frequency is at 131.550 Mhz.
- Adjust the RTL-SDR tuner gain under the SDRSharp configure button for best reception.
- Set the receive mode to AM. For now turn OFF the squelcher and turn OFF Filter Audio. You may experiment later with the squelcher on and with audio AGC if you’d like.
Note, if you are experienced with SDR-RADIO, you may want to use it instead of SDR#. With SDR-RADIO you can output multiple ACARS frequency channels to the same audio device instead of just one. This will increase the number of decoded messages you get.
There are many software packages that can be used to decode the received ACARS packets. PlanePlotter is one good decoding program. It has a trial period of 21 days after which you must purchase a licence for 25 euros. Acarsd is a free decoding program, however we find its decoding performance to be inferior when compared to PlanePlotter, but some other users have reported the exact opposite so it may or may not work for you. AirNav ACARS is another paid decoding program, but is a little pricer than PlanePlotter.
Using PlanePlotter to Decode ACARS
Go to the PlanePlotter website, scroll down and download and install the latest PlanePlotter version.
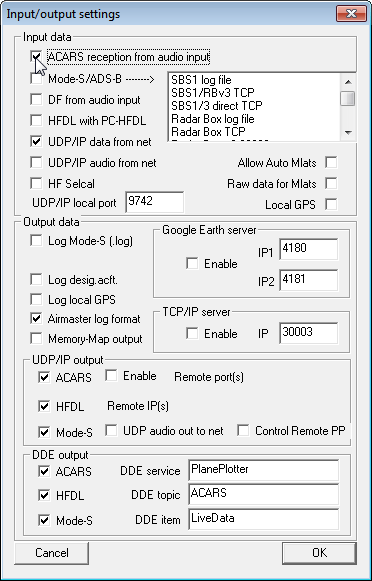
- Open PlanePlotter. Click on the “I/O Settings” icon that looks like a spanner with an ‘i’ to its left. You can see the icon name by hovering over it with your mouse.
- Ensure that the option “ACARS reception from audio input is checked”. Push OK.
- Go to Options->Audio->ACARS->Source. Ensure that the audio source SDRSharp is outputting to is selected.
- Press the “Start” button which is the green circle icon. This will start the decoding.
- Press the “Signal” icon which is the icon to the right of the start button. This shows a graph of signal volume. Ensure the signal is not too loud. This image shows an appropriate volume level for the static in between data packets. You will know the volume is too loud if the graph begins clipping/saturating (signal will look squarish) when ACARS packets are received.

- Now you can look at either the “Message View” or “Aircraft View” which are the two icons next to the Signal icon to see the decoded information.
- Right clicking on an entry in the Aircraft View tab will bring up an internet browser with information about that particular aircraft.

Using ACARSD to Decode ACARS
ACARSD is a free ACARS decoding program. Personally, I find that it decodes less ACARS messages compared to the paid options, but other users have reported the exact opposite, so it is best if you try it out for yourself. If you would still like to try this software as it is free, follow the instructions below.
Go to the acarsd website and download and install acarsd. Make sure to follow the instructions on the website for installing.
- Ensure your default audio device is set correctly in windows sound recording properties. Acarsd will use the first default audio device found. You may need to set your sound card to use 44100 Hz sampling and check this setting in the acarsd set up as well.
- Run acarsd.exe in your acarsd folder to open acarsd.
- Adjust the volume in SDRSharp or Windows so that the volume reading in the bottom right corner of the acarsd window is at around 0-10 for static. If the volume is too loud, acarsd will not decode the ACARS message.
- Decoded ACARS packets should begin to show up.
The number of decoder passes can be changed in Windows->acarsdgui settings. Setting it higher may improve decode performance.
If you need a free ACARS decoder, you may be able to try rtl_acars or acarsed for Linux, but these are harder to set up.
Some ACARS Tips
- You will need a decent outside antenna to get good signal strength. A discone, j-pole or colinear antenna placed up high and tuned to the airband frequencies may be good options to research.
- ACARS packets usually do not contain location information. If you are interested in tracking aircraft like a radar using RTL-SDR, see ADSB decoding.
- Most of the actual ACARS messages will be displayed as gibberish. These messages are intended for the on board avionics computers and ground telemetry.
- Note that receiving ACARS in some countries may be illegal. Please decode responsibly.
- Once you get the hang of ACARS with SDRSharp, you may want to switch to SDR-RADIO. The reason that SDR-RADIO may be better is that it is possible to listen to up to six ACARS channels simultaneously with multiple VFOs. Just send the VFO audio to the same audio output device.
ACARS Frequencies
Most ACARS packets will be on the primary 131.550MHz frequency. But around the world, various other frequencies are also used.
| FREQUENCY | REGION / COUNTRY |
|---|---|
| 131.550 | Primary Channel worldwide |
| 129.125 | Additional channel for USA & Canada |
| 130.025 | Secondary channel for USA and Canada |
| 130.425 | Additional channel for USA |
| 130.450 | Additional channel for USA & Canada |
| 131.125 | Additional channel for USA |
| 131.450 | Primary channel for Japan |
| 131.475 | Air Canada company channel |
| 131.525 | European secondary |
| 131.725 | Primary channel in Europe |
| 136.700 | Additional channel for USA |
| 136.750 | Additional channel for USA |
| 136.800 | Additional channel for USA |
| 136.900 | European secondary |
| 136.850 | SITA North American Frequency |
| 136.750 | New European frequency |
| 131.850 | New European frequency |
Table Source: Acarsd
Other Decoding Software
General purpose ham software like MultiPSK and pager decoding software PDW can also decode ACARS packets. However, these generally do not link to an aircraft spotting website.
There are also the Linux based command line based programs such as rtl_acars and acarsed. Acarsed
 If you enjoyed this tutorial you may like our ebook available on Amazon. The Hobbyist’s Guide to the RTL-SDR: Really Cheap Software Defined radio. |
The post RTL-SDR Tutorial: Receiving Airplane Data with ACARS appeared first on rtl-sdr.com.